How To Find How Much RAM I Have Installed on Windows PC?

RAM is one of the most essential system resources required to run programs. All software packages list RAM in their system requirements. If your Windows PC doesn’t match the minimum RAM specification for a chosen software package, the program isn’t going to run on it. As such, you should check how much RAM your system has before installing proprietary software at least. This is how you can find out how much RAM a Windows desktop or laptop has.
The Control Panel’s System Tab
The Control Panel’s System tab includes a few basic specifications, which include installed RAM, CPU and system type. To open the System tab, press the Win key + X hotkey in Windows 10 and then select Control Panel from the menu. That will open the Control Panel window shown in the snapshot directly below.
Click System to open the tab in the snapshot below. Note the installed RAM specification on that tab. That includes the standard specification, which will be something like 4, 8 or 16 GB, and your usable RAM.
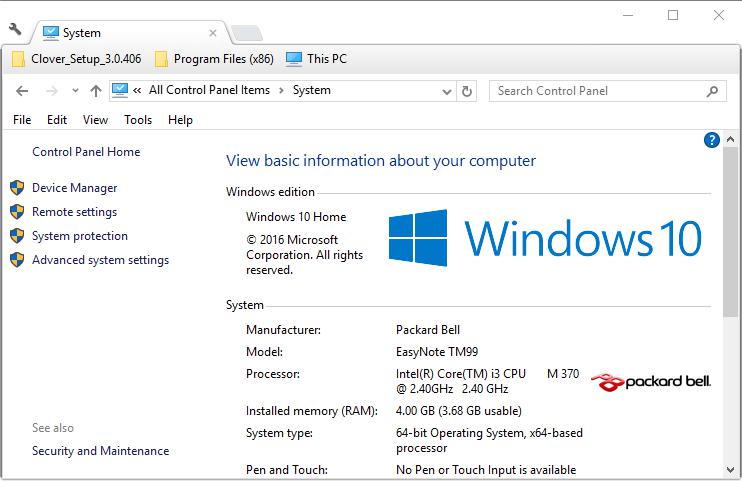
Also note that 32-bit Windows might under report the actual amount of RAM. The 32-bit Windows versions are limited to a maximum 4 GB RAM. So even if your desktop or laptop has 8 GB RAM, the 32-bit Windows OS can only make use of half that.
The Settings App
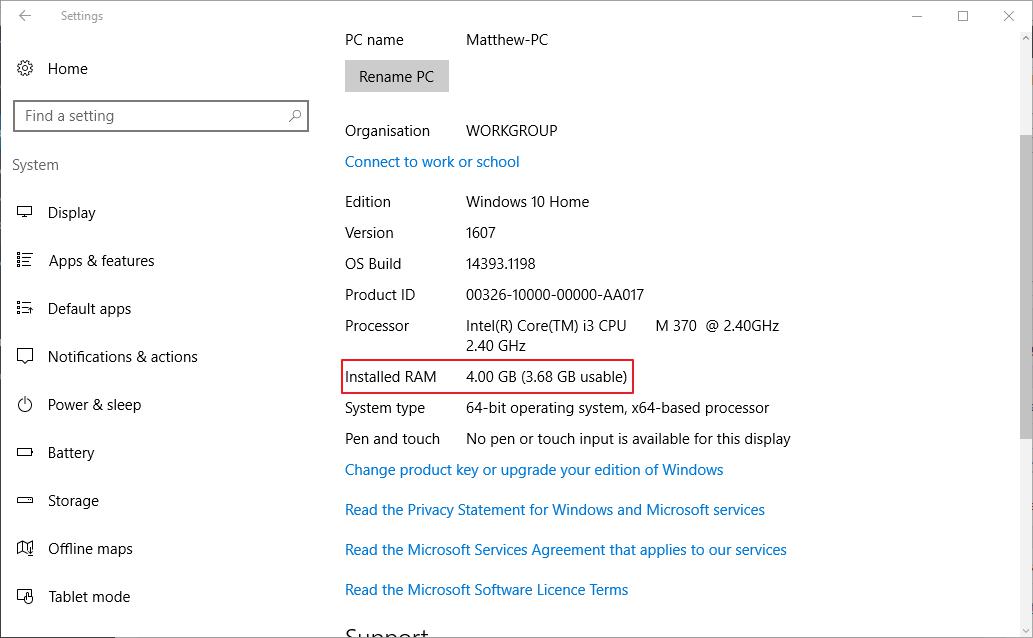
The Windows 10 Settings app lists the installed RAM specification and a few other system details. You can open those system details in the Settings app by pressing the Start button and clicking Settings. Then select System > About to open the specifications in the snapshot below. That specifications list includes the Installed RAM spec.
The System Information Window
If you need to check RAM and other specifications, open the System Information window. That provides much more detailed specifications than the Control Panel’s System tab and the Settings app. You can open System Information by pressing the Win key + R hotkey and entering ‘msinfo32’ in Run’s text box. Press OK to open the window directly below.
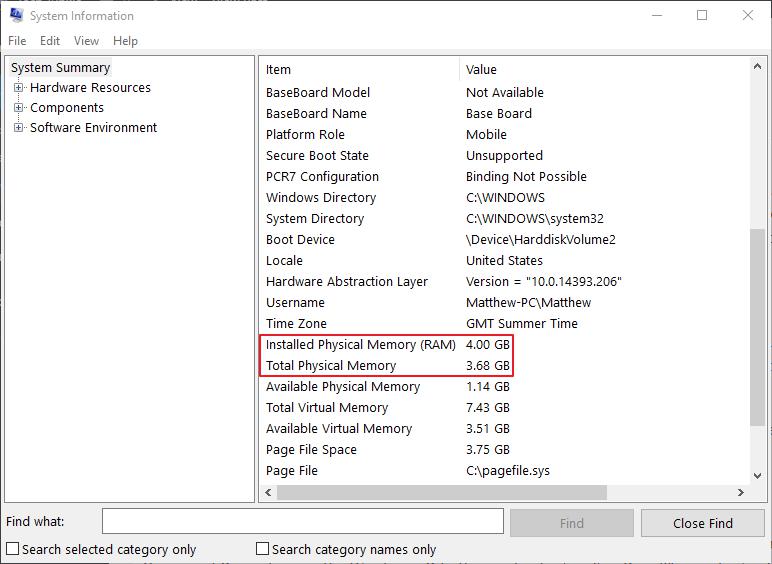
Click System Summary to open a list of specifications. The RAM specification is a little further down the list, so scroll down the window a little. The summary includes the same RAM specifications as the Control Panel’s tab, but also provides lots more system details.
You can print those system specifications by clicking File > Print. Alternatively, export them to a text file by selecting File > Export. Enter a title for the text document and press the Save as button.
Check RAM Specifications with the Command Prompt
You can also find out how much installed RAM your laptop or desktop has via the Command Prompt. To open the Command Prompt, press the Win key + R hotkey and enter ‘cmd’ in Run. Then enter ‘systeminfo’ in the Prompt and press the Return key. The Command Prompt will display general system specifications as in the screenshot directly below.
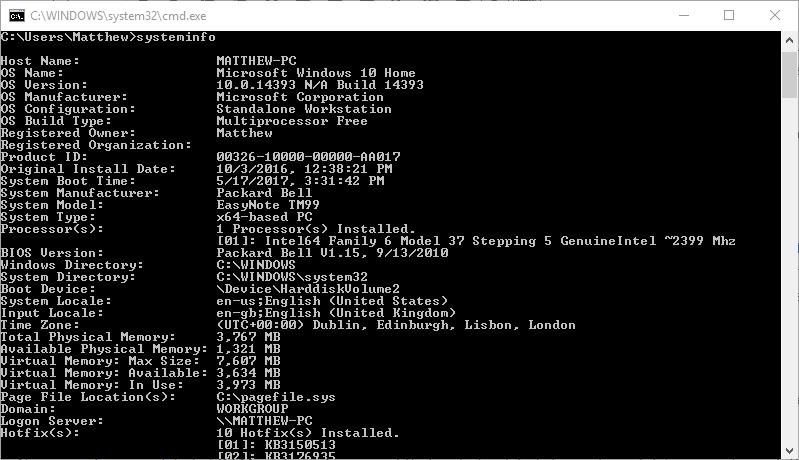
Your usable RAM is listed there with the Total Physical Memory spec. Note that the specification is also in megabytes, not gigabytes, so it will be something like 3,767 megabytes (otherwise 3.7 GB).
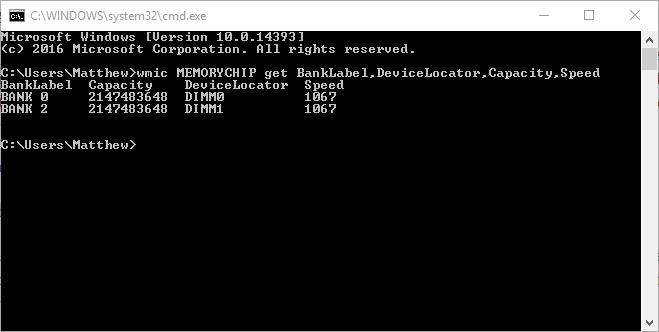
You can get a more detailed RAM configuration report that includes details for each module’s size and speed. Enter ‘wmic MEMORYCHIP get BankLabel,DeviceLocator,Capacity,Speed’ in the Command Prompt. That presents you with the details in the snapshot directly below. There the amount of RAM for each module is listed as a more exact figure. Those extra configuration details might come in handy for upgrading RAM.
Check Current RAM Usage With the Task Manager
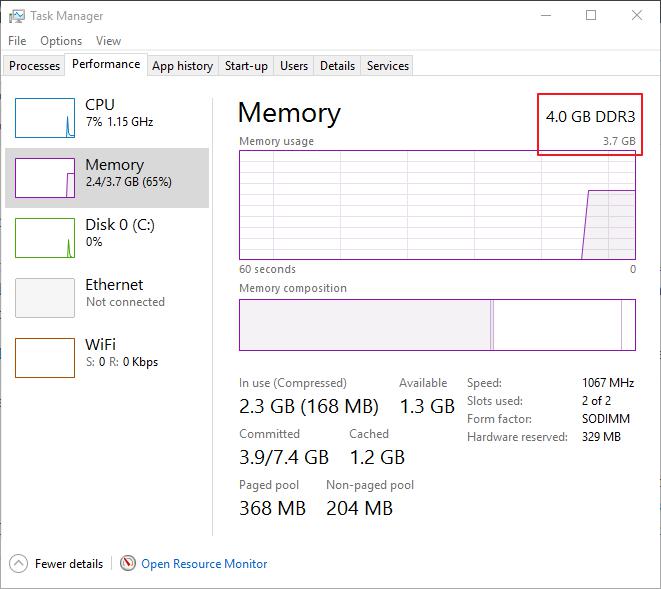
The Task Manager is a handy system utility that provides RAM usage details. So this also includes your desktop or laptop’s usable RAM specification. You can open the Task Manager in Windows 10 or 8 by pressing the Win key + X hotkey. Select Task Manager on the menu to open the system tool.
Select Task Manager’s Performance tab and click Memory to open usage statistics shown in the snapshot below. That includes your PC’s total and usable RAM specifications. This also tells you how much current RAM is in use and how much is available. This system tool guide provides further Task Manager details.
So that’s how you can find out how much RAM a desktop or laptop has and check other system details in Windows. Then you can compare that specification with software system requirements. You won’t be able to run any software that has a higher RAM specification than the Windows PC. In addition to RAM, check a program’s platform compatibility and CPU system requirements before purchasing it.