How to Find Mac Uptime in OS X

System uptime, the amount of time since a computer’s last boot up, can be an important piece of information for troubleshooting and maintenance purposes, as well as grounds for bragging rights. While Apple has made rebooting OS X far less inconvenient than it used to be with features such as the ability to automatically re-open your last-used apps at login, some Mac owners may be curious about just how long their system has gone without a reboot. Here are two ways to find that information in OS X.
Find Mac Uptime via System Information
Perhaps the quickest way to find your Mac uptime value is to use the OS X System Information utility. To get there, hold the Option key on your keyboard and click the Apple icon at the far left of the OS X Menu Bar. Select System Information.
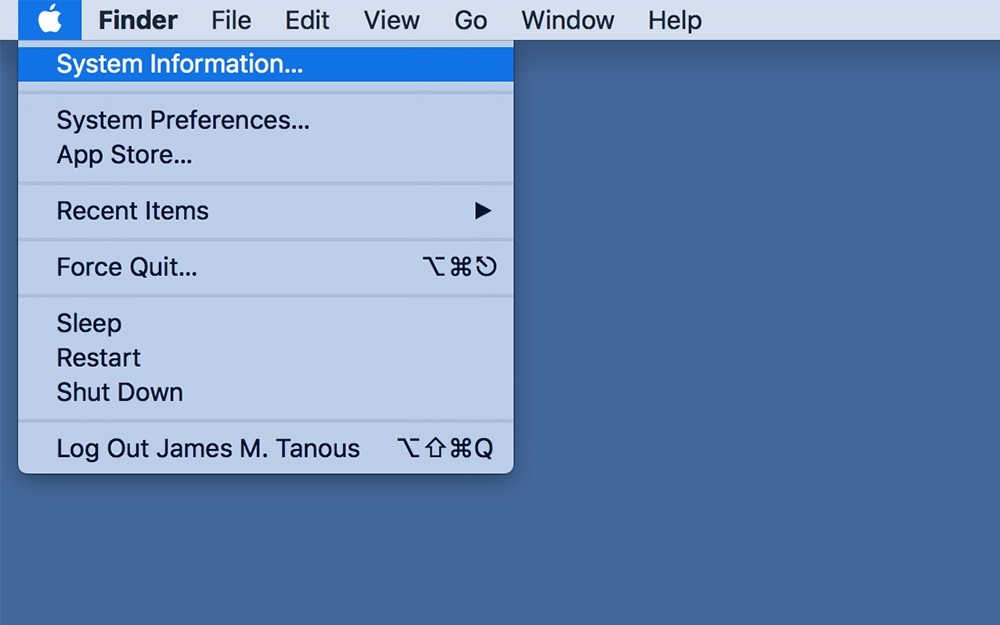
You can also launch the System Information utility by clicking on the Apple icon in the Menu Bar without holding the Option key, selecting About This Mac, and then clicking System Report.

In the System Information window, find and click on Software in the list of sections on the left of the window. This will reveal key information about your Mac and the current installed version of OS X on the right of the window.
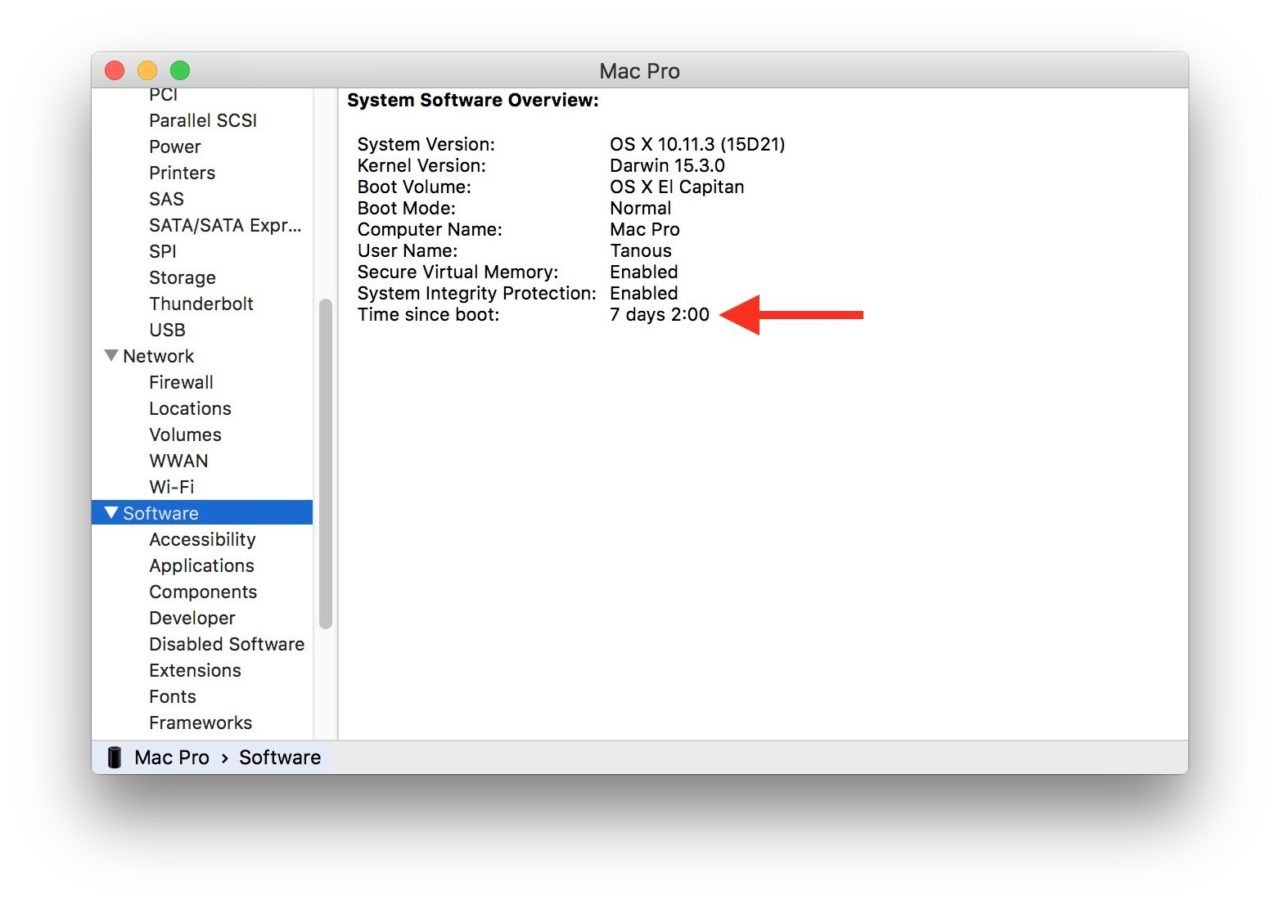
Listed among this information is an entry labeled Time Since Boot with a value in days, hours, and minutes. In the case of our example screenshot above, we can see that our Mac’s current uptime is 7 days, 2 hours, and 11 minutes.
Note that this value reflects the uptime at the moment that you launch the System Information utility, and that it won’t update in real-time as you keep the utility open. Therefore, if System Information is already open when you want to check your Mac’s uptime, make sure you quit and relaunch it to refresh the uptime value so that you’re looking at accurate information.
Find Mac Uptime via Terminal
For the command line lovers out there, you can also find your Mac uptime value via a Terminal command. Just launch Terminal, type uptime, and press Return on your keyboard to execute the command.
You’ll see a new line appear in the Terminal window below your command reporting how long your computer has been “up.” In our example screenshot above, our Mac uptime is 7 days, 2 hours, and 1 minute. This method may be more useful than the System Information method above because, while this value also won’t update in real-time, it provides you with a time stamp (in our case, 11:02) of when the uptime report was generated.
The Terminal uptime method also gives you more information that may be useful for troubleshooting. Specifically, it provides both the Mac’s number of user accounts at the time of the check, as well as “load averages” calculations, which are UNIX-based values that show the average amount of work that your Mac demanded of the CPU in the past 1, 5, and 15 minutes, respectively. The way that load averages work and the meaning of the numbers will vary based on the amount of processors and cores available to the system, and a deeper explanation is beyond the scope of this tip. For more on load averages in UNIX-based operating systems, check out this article.













One thought on “How to Find Mac Uptime in OS X”