How to Overclock Your Laptop Running Windows 11

While overclocking a PC is generally easy (provided that you have hardware that supports it), even finding out if you can overclock a laptop can be a nightmare. Let’s delve into this laptop overclocking guide to dispel a few myths and show you if it can really be done (or if you need alternatives).
Can You Overclock a Laptop?
In general, the answer is no. A vast majority of laptops (barring the extremely high-end models) come with locked CPUs and other hardware that prevent any modifications to the manufacturer’s installation. In other cases, the BIOS itself, which is the primary way to overclock a CPU on a PC, doesn’t come with the necessary settings.
So, how will you know if a laptop you plan on purchasing can be overclocked? Most manufacturers will actively advertise that fact somewhere in the paperwork, so you can look up the exact model on the manufacturer’s website to be sure.
Alternatively, there are two main ways to check if a laptop you already have can be overclocked.
Method 1. Turbo Button
Some laptops, notably from the gaming-oriented brand Acer, come with a dedicated Turbo hotkey on their keyboards.

Pressing this button will overclock the CPU to its maximum rated clock (as set by the manufacturer). In some cases, this can overclock the CPU by around 40-50%.
Step 1. Open the PredatorSense app on your device and make sure the Turbo setting is available.
Step 2. Hit the Turbo button.
Step 3. When you don’t need to overclock the laptop anymore, press the button again and close the app.
Overclocking in this way is generally safe, as it’s supported by the manufacturer, but severely increases the power draw of the laptop and should be used sparingly when working with extremely demanding programs that cause it to lag noticeably.
On some laptops, the Turbo will also be called “Boost.”
Method 2. Manufacturer App
The two major CPU manufacturers (Intel and AMD) have software that can help you overclock your PC. Incidentally, it can also detect whether your laptop is overclockable in the first place:
- Intel’s software is the Extreme Tuning Utility, or XTU.
- AMD uses the Ryzen Master, since mainly Ryzen cores can be overclocked.
Step 1. Go to the website your CPU’s manufacturer website and download the applicable software.
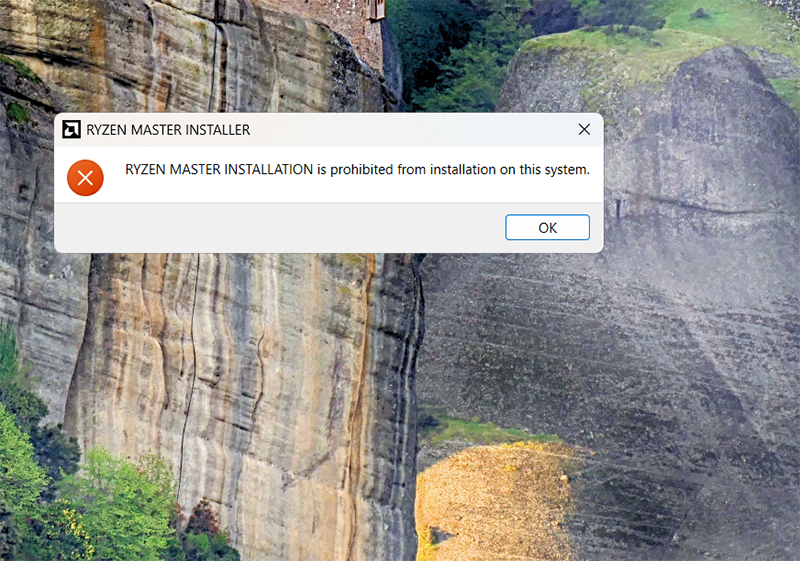
Step 2. Try to run the installer.
Step 3. If you receive an error, your laptop can’t be overclocked.
Step 3a. If you can install the software normally, run it, go to “Manual” mode, and start increasing the core’s clock by small amounts (25 to 50 MHz).
Step 4. Run benchmarking software like 3DMark or Cinebench to check the new clock performance and adjust if needed. CPU stress testers and temperature monitors (Prime95, AIDA64, CoreTemp, HWMonitor) can help you determine if the system is stable long-term.
Limitations and Precautions
It should be noted that overclocking doesn’t depend on your operating system. However, with many higher-end models only naturally supporting a better operating system, older laptops that can’t run Windows 10 or 11 might not have the option in the first place.
Additionally, overclocking will generally increase the resource requirements of your laptop, drastically shortening its battery life.
Finally, an overclocked laptop will also heat up more, so you might find it no longer usable while on the lap when the CPU is running at its new full speed.
If your laptop starts overheating, it will shut down to prevent damage. In that case, you’ll need to undo the overclocking and/or clean its exhaust fan.