Router Not Working – How To Troubleshoot your Router

The massive increase in internet-enabled devices means many homes now have both a modem and a router. Where once we were connecting a single computer to our internet modem, we now need multiple physical and wireless connections to satisfy our need to be online all the time. That means everyone should know some basic router troubleshooting and that is what today’s tutorial is all about.
Routers can be very complicated but work on simple principles. If we cover the basics and some common problems here, hopefully you should be able to troubleshoot many of the issues we come across on a daily basis. So here are some common scenarios to help keep your home network running smoothly.
As different routers have different interfaces it is impossible to give you specific instructions on how to make changes. I will show you what you need to do but I’m afraid it is up to you to find out how. Your router manual or support website should have the answers. I generally do not like making tutorials that aren’t actionable, but the sheer variety of routers out there makes doing that impossible.
If you cannot connect to the internet
If you wake up one morning and cannot connect to the internet, a few basic checks can help a lot.
First, check the device you are using to connect. Is it the only one that cannot access the internet or are other devices affected? If it is just that device, reboot it and retest.
If it is all devices, check your modem and router to make sure both are powered on and active. Usually, both will display white or green lights. Amber or orange lights are warning lights and red are usually more serious.
If the router or modem lights are all normal, switch both devices off for 10 seconds. Power them on again, give them both at least 60 seconds to download config files from the ISP and begin working. If all lights are green, retest.
Intermittent connection issues
Intermittent connection issues could be any number of things but we should check the basics as part of our troubleshooting.
- Check the power to the router and modem is secure and not loose.
- Check all Ethernet cables are secure and not loose.
- Monitor activity lights on both router and modem. If the connection light goes orange periodically on your modem, it is the network at fault and not your devices.
- Reboot the devices accessing the network.
In standard wired networks, one of these steps will usually fix the issue.
In wireless networks, intermittent connections are usually caused by router configuration. Log into your router and check any logs. Look for ‘disconnection’, ‘reset’, ‘config’ and words like that. Reboot your router if you see them and monitor.
Change the wireless channel. From your router’s wireless configuration page, shift the wireless channel a couple along and retest. In apartment buildings or places where there are a lot of networks, they can clash which can cause outages.
If you have a smartphone, there are apps that can sniff wireless networks to see what channels are in use. Consider one of these, assess what channels are in use and shift yours so at least two channels are between yours and the closest others.
Can access the internet but not websites
This is a very common occurrence but isn’t necessarily down to the router. This symptom is usually down to DNS (Domain Name Service) that turns URLs into IP addresses.
- First check whether it is just one device or many devices that can access the net but not web pages.
- If it is just one device, reset it. If it’s a phone, reboot the phone. If it’s a computer, either reboot the computer or disable the network card and then enable it again.
- If it is multiple devices, check lights on both router and modem. Reboot if there are any issues.
- If you use your ISPs DNS server, reboot your modem.
- If you use third-party DNS through your router, reboot your router.
- If that doesn’t work, log into the device that controls DNS and add 8.8.8.8 and 8.8.4.4 as DNS addresses and retest. These are Google’s DNS servers. If yours are already set to Google, try 208.67.222.222 and 208.67.220.220 for OpenDNS.
Changing DNS server or refreshing DNS with a reboot should fix the issue. If not, changing DNS server will surely do the trick. Depending on how you have your network set up, DNS will be controlled either by your router or modem. Check both of them to see which is performing DNS duties.
Slow wireless connection
Slow wireless connections are incredibly frustrating but they don’t always mean something is wrong. Sometimes, too many people are trying to do too much at once. A few basic router troubleshooting steps should tell you.
Check wired access. Is it also slow or fast? If Ethernet is slow too, the ISP may be having problems. You could reboot both router and modem to make sure.
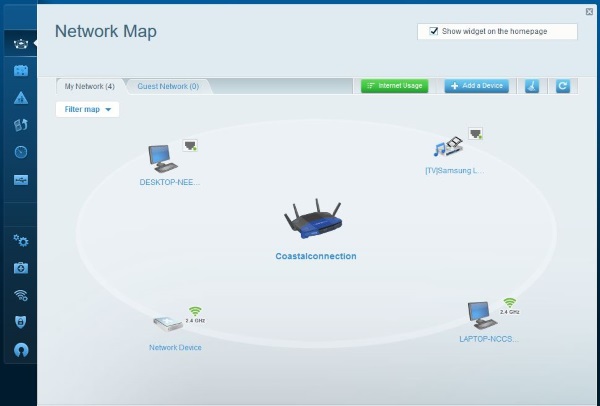
Log into your router and see how many people are connected. Your router should have the ability to show connected devices or a network map. This is also useful to see if anyone is using your wireless network who shouldn’t be.
Perform the checks mentioned above for checking and changing wireless channel. There may be a new connection interfering with yours. Change the channel if necessary.
Consider moving the aerials or router itself. Getting the router position right takes practice. Experiment with positioning to get the best result across your building. The larger the house, the more to the center you need to place the router. Angle the aerials for optimum speed if you can too.
General router troubleshooting
If you keep having network issues but cannot figure out why, my final troubleshooting tip involves a factory reset. This can flush out any configuration or firmware errors that can interfere with your network. It is a step of last resort though and should only be attempted once you have exhausted all other tips.
As well as resetting the router it will return all settings back to factory defaults. If you have configured your network to your specific needs you will need to configure it once more. If you have to perform a factory reset, it might be worth noting all the changes you made before doing it. Also be aware that the default user name and password will also return.
Then:
Turn your router around so you can see the back. You should see a recessed pinhole somewhere labeled Reset. Put something long and thin into the hole, press firmly until you feel movement and hold it for 10 seconds. Let go and let the router reboot. This could take a minute or two depending on whether the router updates itself or not. Retest once fully booted.
Basic router troubleshooting can fix the majority of home network issues and is well worth experimenting with. At least now you have a few ideas of what to do if you want to try.