Which Allocation Size Should You Use When Formatting A Hard Drive?
When going to format a hard drive in Windows, the default file allocation unit size is 4096 bytes, however there are a whole bunch of other choices to pick from:
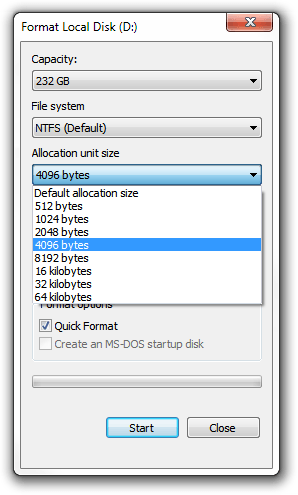
Is there a speed difference?
Yes. Selecting a larger cluster size results in faster access times.
Why is there a speed difference?
Because with larger clusters there are less clusters to record, resulting in less records in the table, resulting in less “work” when retrieving files.
What are the larger cluster sizes best suited for?
Big files, such as ripped DVDs, raw AVI files and things of that sort.
Conversely, if most of what you store is smaller files, the smaller cluster size is more suitable.
Does cluster size affect overall space available?
Yes it does.
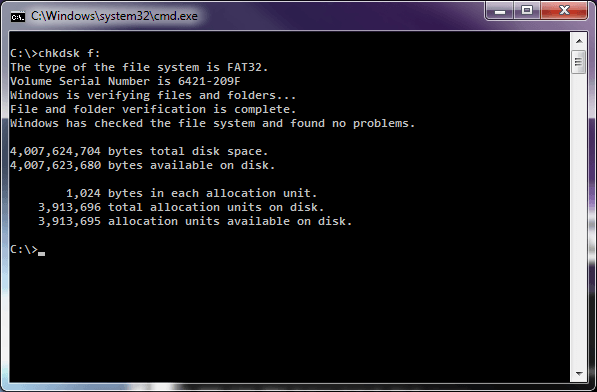
A quick example using a 4GB USB stick:
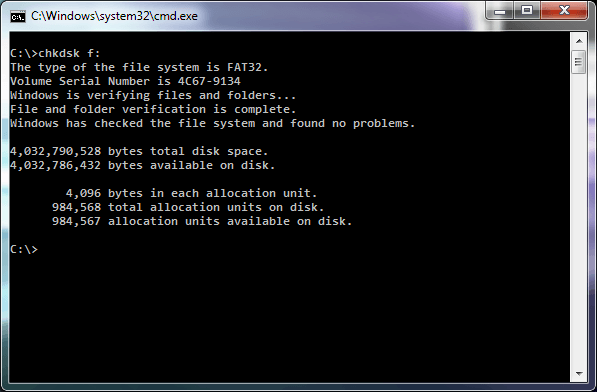
Formatted using 1024 byte cluster
Formatted using 4096 byte cluster
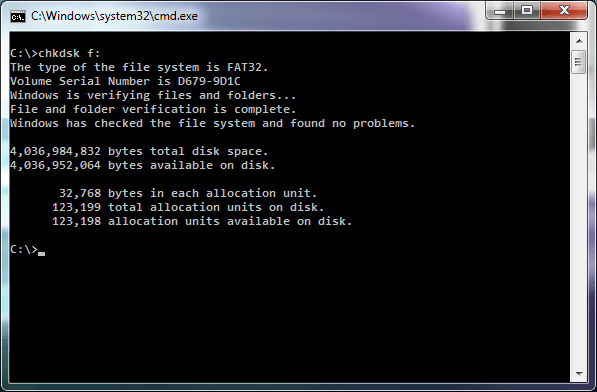
Formatted using 32k file cluster
What if I don’t know which to choose?
This is why the default cluster size is 4096 bytes. If unsure, use 4096.
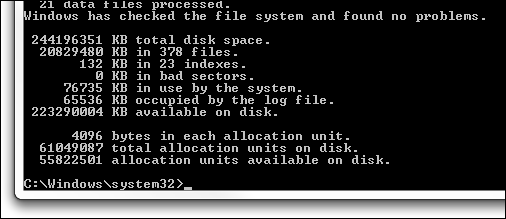
How can I find out what the current cluster size of a hard drive is?
This is done using CHKDSK, as seen above.
1. Launch a Command Prompt. (If using Windows Vista or 7, you must ‘Run As Administrator’).
2. Type CHKDSK (DRIVE LETTER HERE): and press Enter, such as CHKDSK D:
3. The final report at the end of CHKDSK will state the bytes in each allocation unit.













5 thoughts on “Which Allocation Size Should You Use When Formatting A Hard Drive?”
1 file was done in seconds while the 1000-more 1 files done in minutes.
Steve Wohl